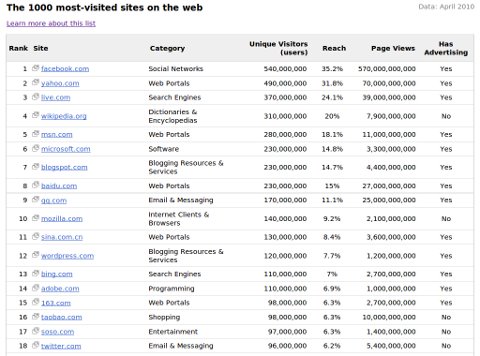
Curious to know what are the largest websites on the web? While there are some lists around, none of them was regarded as accurate, and Google apparently wants to fix this. It just released its own
Top 1000 Websites list.
As you can see below, the list shows the category of the website, its number of monthly unique visitors, page views, and whether or not the website accepts advertising.
The announcement was made on the official
AdWords blog. In fact this list was developed to help advertisers target big websites that accept ads.
According to Google itself “the list excludes adult sites, ad networks, domains that don’t have publicly visible content or don’t load properly, and certain Google sites,” so keep this in mind.
Here are the blogs I spotted on the list:
- #246 – The Huffington Post – 12 million Uniques
- #434 – Engadget – 8,1 Million Uniques
- #540 – Gizmodo – 6.7 Million Uniques
- #696 – Mashable – 5.6 Million Uniques
- #850 – TechCrunch – 4.7 Million Uniques
If these numbers are accurate they reveal some very interesting data. For example, Mashable is as big as PCWorld, one of the oldest and most established tech publications. Similarly, Engadget is as big as the Washington Post (on the web only, obviously). And The Huffington Post as big as Digg (counting uniques only, not page views).
I was hoping to see Daily Blog Tips around the last positions, but no luck…!
Update: Here is where Google says the numbers are coming from:
Traffic statistics are estimated by combining sample user data from various Google products and services and opt-in direct-measured site-centric data. In addition, site owners may opt-in direct measured Google Analytics traffic statistics to provide a more accurate measure of their site traffic. Sites that have opted-in direct measured Google Analytics data are indicated through the footnote “Google Analytics data shared by publisher”.